esphome-sesame3
ESPHome Smart Lock component for CANDY HOUSE SESAME 5 / SESAME 5 PRO / SESAME Bot 2 / SESAME bot / SESAME 3 / SESAME 4 / SESAME Bike, control via Bluetooth LE
[!NOTE] This component does not use ESPHome’s built-in
BTClientfunctionality. Therefore, this component cannot coexist with other BLE components on the same ESP32. Use this component with a separate ESP32 device from other BLE components.
Setup this component
You need to add compiler / library options to ESPHome base configuration, and external_components section link to this component.
external_components:
- source:
type: git
url: https://github.com/homy-newfs8/esphome-sesame3
ref: v0.24.0
components: [ sesame, sesame_ble ]
Build options
The build options differ depending on the version of ESPHome. See the example below.
If you want to use more than four SESAME devices with one ESP32 module, edit the CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_MAX_CONNECTIUONS parameter (It might be a good idea to check the free memory with ESPHome’s Debug component).
Select the ESP32 board you want to use. Choose Arduino or ESP-IDF framework.
ESPHome 2025.10.0 or later
NimBLE must be enabled by sdkconfig_options, and many compile options moved to sdkconfig_options section.
esphome:
platformio_options:
build_flags:
- -Wall -Wextra
- -DUSE_FRAMEWORK_MBEDTLS_CMAC
min_version: 2025.10.0
esp32:
board: esp32-c3-devkitm-1
framework:
type: arduino
sdkconfig_options:
CONFIG_BT_ENABLED: y
CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_ENABLED: y
# Configure the maximum number of connections as required (maximum: 9)
CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_MAX_CONNECTIONS: "6"
CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_CRYPTO_STACK_MBEDTLS: y
CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_ROLE_BROADCASTER_DISABLED: y
CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_ROLE_PERIPHERAL_DISABLED: y
You can select esp-idf instead of arduino.
ESPHome 2025.7.0 to 2025.9.x
esphome:
platformio_options:
build_flags:
- -Wall -Wextra
- -DMBEDTLS_DEPRECATED_REMOVED -DCONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_ROLE_BROADCASTER_DISABLED -DCONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_ROLE_PERIPHERAL_DISABLED
# Configure the maximum number of connections as required
- -DCONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_MAX_CONNECTIONS=4
- -DCONFIG_MBEDTLS_CMAC_C -DUSE_FRAMEWORK_MBEDTLS_CMAC
min_version: 2025.7.0
esp32:
board: esp32-c3-devkitm-1
framework:
type: arduino
external_components:
- source:
type: git
url: https://github.com/homy-newfs8/esphome-sesame3
ref: v0.25.0
components: [ sesame, sesame_ble ]
ESPHome 2025.5.x to 2025.6.x
esphome:
platformio_options:
build_flags:
- -std=gnu++17 -Wall -Wextra
- -DMBEDTLS_DEPRECATED_REMOVED -DCONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_ROLE_BROADCASTER_DISABLED -DCONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_ROLE_PERIPHERAL_DISABLED
# Configure the maximum number of connections as required
- -DCONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_MAX_CONNECTIONS=4
build_unflags:
- -std=gnu++11
min_version: 2025.5.0
(More older versions of ESPHome was supported by old versions of this component (not documented))
Configure for your SESAME
Minimum configuration
sesame:
# Model type identifier
model: sesame_5
# 32 hexadecimal with 4 hyphens (8-4-4-4-12)
uuid: "01020304-0102-0102-0102-010203040506"
# 16 bytes binary in hexadecimal
secret: "0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef"
lock:
id: lock_1
name: Lock1
tag: "My awesome system"
If you are using SESAME OS 2 Devices (SESAME 3 / SESAME 4 / SESAME bike / SESAME bot), you must specify Bluetooth MAC address instead of uuid.
See below for information on how to find the parameters (uuid, secret) for your SESAME.
Configuration variables
- model (Required): Model of SESAME. Use one of:
sesame_5,sesame_5_pro,sesame_bot_2,sesame_bike_2,sesame_face,sesame_face_pro,sesame_touch,sesame_touch_pro,remote,sesame_face,sesame_face_pro,sesame_face_ai,sesame_face_pro_ai,sesame_4,sesame_3,sesame_bot,sesame_bike - uuid (Optional, string): UUID of SESAME.
uuidoraddressmust be specified, see below. - address (Optional for SESAME OS3 models, Required for SESAME OS2 models, string): Bluetooth MAC Address of SESAME.
uuidoraddressmust be specified, see below. - secret (Required, string): See below.
- public_key (Required for SESAME OS2 models, string): See below.
- timeout (Optional, Time): Connection to SESAME timeout value. Defaults to
10s. - connect_retry_limit (Optional, int): Specifies the number of connection failures before reboot the ESP32 module. Defaults to
0(do not reboot). - always_connect (Optional, bool): Keep connection with SESAME. Must be
truewhen this component containslockobject. Defaults totrue. If set tofalse, disconnect from SESAME after receiving the status (and reconnect ifupdate_intervalis set). - update_interval (Optional, Time): Request SESAME to send current status with this interval. Some devices (SESAME Touch) do not send updated status without this option. Defaults to
never. - lock (Optional, sesame_lock): Lock specific configurations. See below.
- bot (Optional, sesame_bot): Bot specific configurations. See below
Expose SESAME status as sensors
- battery_pct (Optional, Sensor): See below
- name (Required, string): The name of the battery level sensor.
- All other options from sensor
- battery_voltage (Optional, Sensor): See below
- name (Required, string): The name of the voltage sensor.
- All other options from sensor
- battery_critical (Optional, Binary Sensor): SESAME battery critical state is exposed as a binary sensor.
- name (Required, string): The name of connection sensor.
- All other options from binary_sensor
- connection_sensor (Optional, Binary Sensor): SESAME connection state is exposed as a binary sensor.
- name (Required, string): The name of connection sensor.
- All other options from binary_sensor
Lock specific variables
For lock devices (sesame_5, sesame_5_pro, sesame_4, sesame_3, sesame_bot, sesame_bike, sesame_bike_2), lock functionality can be used.
In addition to base Lock variables:
- tag (Optional, string): Tag value recorded on operation history. Defaults to “ESPHome”. If you want to use various tag values on automation, see below.
- history_tag (Optional, Text Sensor): See below
- name (Required, string): The name of the history tag text_sensor.
- All other options from text_sensor
- history_type (Optional, Sensor): See below
- name (Required, string): The name of the history type sensor.
- All other options from sensor
- trigger_type (Optional, Sensor): Deprecated. Use history_tag_type instead.
- history_tag_type (Optional, Sensor): See below
- name (Required, string): The name of the history type sensor.
- All other options from sensor
- fast_notify (Optional, bool): Notify lock status immediately on detecting status changed. If false and
history_tagorhistory_typedefined, lock notification is postponed until history information has been received. Default isfalse. - unknown_state_alternative (Deprecated, Optional, lock_state): (As of Home Assistant 2025.10.0,
NONEstate is properly treated asUNKNOWN)
If the lock state of SESAME is unknown (for example, before connecting or during disconnection), this module notifies HomeAssistant of theNONEstate. Currently, HomeAssinstant seems to treat theNONEstate as “Unlocked”.
If you don’t want it to be treated as “Unlocked”, you can send the unknown state as any other state (candidates:NONE,LOCKED,UNLOCKED,JAMMED,LOCKING,UNLOCKING). If not set as this variable, this module will not sendLOCKINGandUNLOCKING, so you can write automation scripts that interpret these values as “UNKNOWN”. - unknown_state_timeout (Optional, Time): If you do not want disconnection from SESAME to be immediately treated as unknown, set a timeout value with this variable. Defaults to
20s.
Bot specific variables (From v0.11.0)
For sesame_bot, you can specify lock or bot.
For sesame_bot_2, bot can be used.
See bot usage for detailed example.
- bot: Bot settings section marker.
- id (Optional, string): Specify the ID for code generation.
- running_sensor (Optional, Binary Sensor): Expose
ONvalue while Bot is running.
Identify parameter values for SESAME devices
uuid
You can find the UUID using the SESAME smartphone app. Open the details screen of the SESAME you want to control and use the string listed in the UUID field. The UUID is a string consisting of hexadecimal numbers and hyphens, as shown below.
01020304-0506-0708-0a0b-0c0d0e0f0102
If you write the wrong value, the connection will fail, so please double check.
If the UUID is displayed abbreviated, try changing the font size on your smartphone to a smaller one.
secret (Secret key of your SESAME)
Secret is PSK for authentication and encryption. You can retrieve your SESAME’s secret from QR code shown on SESAME smartphone app.
Easy way
Use sesame-qr-reader. Display Owner or Manager key on SESAME smartphone app, then upload the QR code image. Use the displayed Secret Key value.
DIY way
Display Owner or Manager key and decode the QR code with any QR decoder. Decoded string is URI like below:
ssm://UI?t=sk&sk=BQECAwQFBgcICQoLDA0ODxAREhMUFRYXGBkaGxwdHh8gISIjJCUm&l=1&n=セサミ 5
Query parameter sk is base64 encoded binary data
(if sk value contains %2B or %2F, replace them with + or /).
Above base64 string is decoded as below:
00000000 05 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
00000010 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f |................|
00000020 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | !"#$%&|
First one byte is model number: 0 = SESAME 3, 2 = SESAME bot, 5 = SESAME 5, and so on. And following 16 bytes are the secret.
The example data above shows that the model is SESAME 5 and the secret is 16 bytes from 01 to 10. So, configuration is:
sesame:
address: 01:02:03:04:05:06
secret: "0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f10"
On SESAME OS2 devices (SESAME 3 / SESAME 4 / SESAME bot / SESAME bike), sk is more long string and decoded binary is 99 bytes. Still the location and length of secret is the same.
public_key (Public key for SESAME OS2 devices)
Public key for encryption. Do not specify this parameter for SESAME OS3 devices (SESAME 5 / SESAME 5 PRO / SESAME Bot 2 / SESAME Touch / SESAME Touch PRO / CANDY HOUSE Remote).
On OS2 devices, you can retrieve key value from QR code.
Easy way
As above, use sesame-qr-reader. Use Public Key value.
DIY way
Decoded OS2 QR code is:
ssm://UI?t=sk&sk=AAECAwQFBgcICQoLDA0ODxAREhMUFRYXGBkaGxwdHh8gISIjJCUmJygpKissLS4vMDEyMzQ1Njc4
OTo7PD0+P0BBQkNERUZHSElKS0xNTk9QUVJTVFVWV1hZWltcXV5fYGFi&l=1&n=セサミ 3
Base64 decoded sk value is:
00000000 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
00000010 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f |................|
00000020 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f | !"#$%&'()*+,-./|
00000030 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f |0123456789:;<=>?|
00000040 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4a 4b 4c 4d 4e 4f |@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNO|
00000050 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 5a 5b 5c 5d 5e 5f |PQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_|
00000060 60 61 62 |`ab|
publik_key is the 64 bytes following the secret, so public_key configuration is:
sesame:
address: 01:02:03:04:05:06
secret: "0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f10"
public_key: "1112131415161718191a1b1c1d1e1f202122232425262728292a2b2c2d2e2f303132333435363738393a3b3c3d3e3f404142434445464748494a4b4c4d4e4f50"
address (Bluetooth MAC Address)
For SESAME OS3 devices (SESAME 5 / Bot 2 / Bike 2), you do not need to specify the Bluetooth MAC address in the yaml.
If you are using a SESAME OS2 device or are unable to specify uuid, continue reading this chapter.
You can identify your SESAME address by using ESPHome BLE tracker with sesame_ble component. First, remove sesame: component definition and add below to your configuration:
logger:
sesame_ble:
(logger must be specified for logging output)
Upload and restart ESP32, logging message contains discovered SESAME devices information:
[08:20:23][I][sesame_ble:107]: 01:02:03:04:05:06 SESAME 5 UUID=01020304-0102-0102-0102-010203040506
Colon separated 6 bytes is Bluetooth address, if you have multiple SESAME devices, distinguish with UUID (You can check the UUID of a SESAME using the SESAME smartphone app).
Configuration for this device will be:
sesame:
address: 01:02:03:04:05:06
[!NOTE]
sesamecomponent cannot coexist with other BLE components includingesp32_ble_tracker. Once you have identified SESAME’s BLE address, you will need to remove the above configuration.</b>
Expose SESAME battery information as sensor value
You can expose SESAME battery remaining percentage and voltage value, then show on your dashboard, use with your automation and etc. (in ESPHome and HomeAssistant)
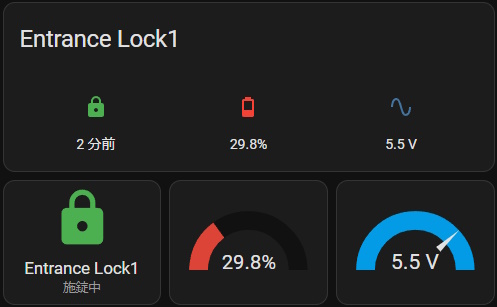
sesame:
⋮
battery_pct:
name: "Lock1_battery_level"
battery_voltage:
name: "Lock1_battery_voltage"
Operation History TAG and History type
[!NOTE] As of the May 2025 firmware, the TAG string specification for CANDY HOUSE devices has changed. See TAG UUID.
You can expose who or what operated SESAME. These values are updated before lock/unlock state. Therefore, you can use history values in your automation’s lock state change actions (You can change this “notify state after tag” behavior by fast_notify option).
sesame:
⋮
lock:
history_tag:
name: "Lock1_history_tag"
history_type:
name: "Lock1_history_type"
History is Lock specific feature, so define these sensors under lock: object.
TAG string
- User name of SESAME smartphone app
- Registered fingerprint name of SESAME Touch
tagvalue of this module- Other API argument (Official Web API, SDK, etc.)
Type value
| Value | Name | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | NONE | |
| 1 | BLE_LOCK | By BT API (Smartphone app, SESAME Touch, this component, etc.) |
| 2 | BLE_UNLOCK | By BT API (Smartphone app, SESAME Touch, this component, etc.) |
| 3 | TIME_CHANGED | |
| 4 | AUTOLOCK_UPDATED | |
| 5 | MECH_SETTING_UPDATED | |
| 6 | AUTOLOCK | |
| 7 | MANUAL_LOCKED | By hand |
| 8 | MANUAL_UNLOCKED | By hand |
| 9 | MANUAL_ELSE | |
| 10 | DRIVE_LOCKED | SESAME bot / SESAME 3 / SESAME 4 |
| 11 | DRIVE_UNLOCKED | SESAME bot / SESAME 3 / SESAME 4 |
| 12 | DRIVE_FAILED | (SESAME bot) / SESAME 3 / SESAME 4 |
| 13 | BLE_ADV_PARAM_UPDATED | |
| 14 | WM2_LOCK | By smartphone app (via Wi-Fi Module 2) |
| 15 | WM2_UNLOCK | By smartphone app (via Wi-Fi Module 2) |
| 16 | WEB_LOCK | By Official Web API |
| 17 | WEB_UNLOCK | By Official Web API |
| 18 | BLE_CLICK | SESAME bot (Not listed in Android API) |
| 21 | DRIVE_CLICKED | SESAME bot (Not listed in Android API) |
History TAG UUID and history tag type
In the original specification, trigger devices (Touch, Remote, Open Sensor) sent their own name or the registered trigger (fingerprint, IC card) name to the SESAME lock/bot. In May 2025, this specification was changed, and trigger devices now send UUIDs instead of their own names or trigger names (and of cource Face).
A similar change was applied to history retrieval. Therefore, there are two types of history tag values that this component receives.
- Literal string (0~30letters)
- UUID (128bits) + History tag type
graph LR
lock[SESAME 5 / bot 2]
t[Old triggers] -->|"lock command(TAG string)"| lock
n[New triggers<br/>After May 2025] -->|"lock command(TAG UUID + trigger_type)"| lock
r[esphome-sesame3] -->|"lock command(TAG string)"| lock
esphome[esphome-sesame3]
lock -->|TAG string or<br/>TAG UUID + trigger_type| esphome
On ESPHome, history_tag_type is represented with float value, and your can determine which history tag type is received by it’s value.
# define lock
sesame:
model: sesame_5
lock:
id: lock_1
history_tag:
id: history_tag_1
name: history tag 1
history_type:
id: history_type_1
name: history type 1
history_tag_type:
id: history_tag_type_1
name: history tag type 1
on_value:
then:
- lambda: |-
if (std::isnan(id(history_tag_type_1).state)) {
// TAG string received
ESP_LOGD("test", "tag string = %s", id(history_tag_1).state.c_str());
} else {
// TAG UUID + history_tag_type received
ESP_LOGD("test", "uuid = %s, type = %d", id(history_tag_1).state.c_str(), (int)id(history_tag_type_1).state);
}
History tag type values
Cited from Protocol specification.
| Value | Name | Device |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | nfc_card | Touch / Face |
| 1 | fingerprint | Touch / Face |
| 2 | password | Touch PRO / Face PRO |
| 3 | face | Face |
| 4 | palm_vein | Face |
| 5 | touch_pro_lock | Touch PRO |
| 6 | touch_lock | Touch |
| 7 | open_sensor | Open Sensor |
| 8 | face_pro_lock | Face PRO |
| 9 | face_lock | Face |
| 10 | remote | Remote |
| 11 | remote_nano | Remote nano |
| 12 | biz_user | |
| 13 | web_api | |
| 14 | android_ble | |
| 15 | ios_ble | |
| 16 | android_wifi | |
| 17 | ios_wifi |
SESAME bot usage
As lock device
When lock setting is specified for sesame_bot device, you can use lock.open action in addition to lock.lock and lock.unlock actions. lock.open performs the same action as tapping the button on the smartphone SESAME app.
sesame:
model: sesame_bot
⋮
lock:
name: some name
Run the script directory
The sesame_bot_2 device cannot be used as lock device. You can specify bot settings instead.
sesame:
model: sesame_bot_2
⋮
bot:
id: bot_2
running_sensor:
name: Bot2 is running
The id bot_2 can be referenced from lambda sections (see below and below).
The sesame_bot devices can also be used with the bot settings.
When used with the bot setting, the device will not expose the lock functionality (Lock/Unlock buttons will not automatically appear in Home Assistant).
To control a Bot, actions must be defined. You can define action button or API service.
Define Bot buttons on ESPHome
SESAME bot 2 has 10 moving scripts (Can edit on smartphone app). Define button on specific script as follows (Script numbers range from 0 to 9 for sesame_bot_2 devices, and from 0 to 2 for sesame_bot devices).
button:
- platform: template
name: "Run Bot2 Script1"
on_press:
- lambda: |-
id(bot_2).run(0);
- platform: template
name: "Run Bot2 Script3"
on_press:
- lambda: |-
id(bot_2).run(2);
- platform: template
name: "Run Bot2 Default Script"
on_press:
- lambda: |-
id(bot_2).run();
Call run() without argument invoke the default script (Selected by smartphone app).
On Home Assistant above buttons appear as follows:
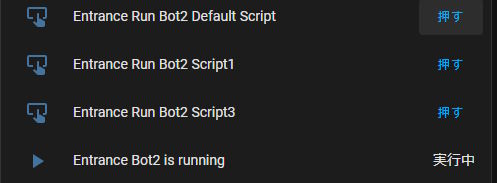
The running_sensor value is also shown (Bot2 is running).
Define Bot service callable from HomeAssistant
api:
services:
- service: run_bot2_script
variables:
script_no: int
then:
lambda: |-
id(bot_2).run(script_no);
Above service can be called from Home Assistant as below:
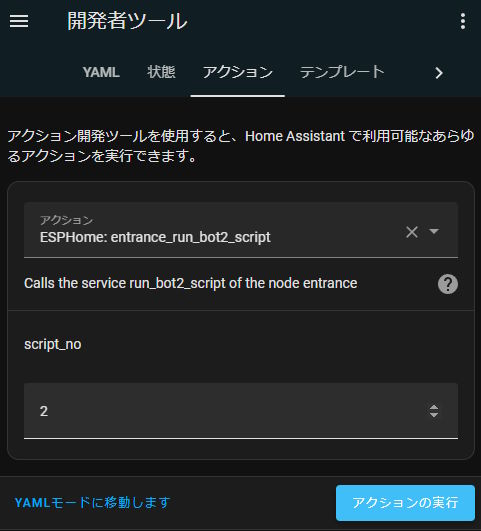
Using various tag values on operation
SESAME records the TAG string of each operation in the operation history. If you want to use different TAG values for automation, call lock, unlock, click functions directory from lambda. Below is a sample service definition that can be called from Home Assistant.
esphome:
name: entrance
api:
services:
- service: sesame_with_tag
variables:
is_lock: bool
tag: string
then:
lambda: |-
if (is_lock) {
id(lock_1).lock(tag);
} else {
id(lock_1).unlock(tag);
}
sesame:
⋮
lock:
id: lock_1
name: Lock1
⋮
This service will be seen as esphome.entrance_sesame_with_tag on Home Assistant (“entrance” is the entity name of ESPHome device).
# Example Home Assistant Service Call to toggle lock
service: esphome.entrance_sesame_with_tag
data:
is_lock: ""
tag: "***Anything***"
You can make lambda call lock/unlock with history_tag_type and tag.
id(lock_1).lock(history_tag_type, tag);
id(lock_1).unlock(history_tag_type, tag);
See explanation of history_tag_type. It’s useful when relaying requests in esphome-sesame_server.
Multiple SESAME conotrol
If you want to control multiple SESAME devices by one ESP32, define multiple sesame objects:
sesame:
- id: lock1
model: sesame_5
address: "ab:cd:ef:01:02:03"
secret: "0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef"
battery_pct:
name: Lock1_battery_level
lock:
name: Lock1
id: lock_1
tag: "My awesome system"
history_tag:
name: Lock1_history_tag
- id: touch1
model: sesame_touch
address: "12:34:56:78:9a:bc"
secret: "0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef"
battery_pct:
name: Touch1_battery_level
update_interval: 12h
The id: of the sesame object is not required. However, it is used as a logging prefix, which is useful for troubleshooting in multiple device environments.
[05:23:27][D][sesame1:317]: connecting
[05:23:31][D][sesame1:321]: connect done
[05:23:31][I][sesame1:283]: Authenticated by SESAME
Full example configuration file
See sesame.yaml.
wifi_ssid, wifi_passphrase, sesame_pubkey, sesame_secret, sesame_address must be set according to your configuration. If you know how to use secrets.yaml, use it. If you don’t, edit sesame.yaml (Remove !secret when replace values).
Avoid WiFi issues
This module starts connecting to SESAME after the WiFi connection when ESPHome starts, so it should not interfere with the WiFi connection.
If this module seems to be interfering with your WiFi connection, please try the following settings.
sesame:
setup_priority: 0
⋮
This setting defers the connection to SESAME until the very end of ESPHome’s initialization.
Schema changed on 0.10.0
There are big structural changes in configuration YAML. It’s not difficult to convert to new schema, for example:
OLD:
esphome:
libraries:
- https://github.com/homy-newfs8/libsesame3bt#0.16.0
⋮
external_components:
- source:
type: git
url: https://github.com/homy-newfs8/esphome-sesame3
ref: v0.9.0
components: [ sesame_lock, sesame_ble ]
lock:
- platform: sesame_lock
name: Lock1
id: lock_1
model: sesame_5
tag: "My awesome system"
address: "ab:cd:ef:01:02:03"
secret: "0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef"
battery_pct:
name: Lock1_battery_level
history_tag:
name: Lock1_history_tag
NEW:
esphome:
libraries:
- https://github.com/homy-newfs8/libsesame3bt#0.21.0
⋮
external_components:
- source:
type: git
url: https://github.com/homy-newfs8/esphome-sesame3
ref: v0.12.0
components: [ sesame, sesame_ble ]
sesame:
model: sesame_5
address: "ab:cd:ef:01:02:03"
secret: "0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef"
battery_pct:
name: Lock1_battery_level
lock:
name: Lock1
id: lock_1
tag: "My awesome system"
history_tag:
name: Lock1_history_tag
In summary,
- Update libsesame3bt version.
- External component name changed from
sesame_locktosesame. - Definition starts with
sesame:object. - Lock-specific settings have been moved under the
lock:object. - Non-locking devices (such as SESAME Touch / Remote) are supported. There is no need to define a
lock:object for such devices.
Related
- SESAME access library for ESP32 libsesame3bt
- SESAME 5 / SESAME 5 PRO Smart Lock CANDY HOUSE (SESAME 3 and 4 are End of Sale)